Baking soda, scientifically known as sodium bicarbonate, effectively neutralizes battery acid. When applied to areas affected by corrosion, it triggers a chemical reaction with the battery acid, transforming it into a harmless substance. This reaction not only neutralizes the acid but also facilitates the removal of corrosion, enhancing the longevity of your battery.
As an experienced professional in the field, I’ve come across a multitude of questions related to everyday items and their unexpected uses.
One such question that often arises is, “Does baking soda neutralize battery acid?” It’s a query that might seem out of the ordinary, but the answer holds significant importance, especially for those who deal with batteries regularly.
In this blog post, I will delve into the science behind this fascinating interaction, shedding light on how a common household item like baking soda can effectively neutralize battery acid.
So, whether you’re a curious reader or someone seeking practical solutions, I invite you to join me on this enlightening journey.
What is Battery Acid?
Now that we’ve established a basic understanding of what battery acid is, let’s delve deeper into its composition to gain a more comprehensive insight.

A. battery acid composition
Battery acid, often used in lead-acid batteries, is a crucial component that stores chemical energy for eventual electrical use. This acid is typically sulfuric acid (H2SO4) diluted with purified water to a concentration of around 30-50%. The acid has a pH of 0.8, indicating its strong acidic nature.
Lead-acid batteries consist of two conductive lead plates, known as electrodes, filled with a viscous gel-like substance. The diluted sulfuric acid solution, also known as the electrolyte, is situated between these plates. The separator, another key part of lead-acid batteries, serves as an insulator by preventing the two plates from directly touching one another, which would result in a short circuit.
B. The dangers of battery acid
Battery acid is highly corrosive due to its strong acidic nature. It can cause severe burns, permanent blindness, and internal organ damage if ingested. Moreover, it is highly flammable and may ignite under intense heat or pressure.
The concentration of sulfuric acid in lead-acid batteries is usually around 15%-35%, although it can be as high as 50%. Improper handling of this chemical can lead to severe health hazards, including death.
The dangers of battery acid highlight the importance of handling batteries with care and using appropriate safety measures. In the next section, we’ll explore how baking soda can neutralize battery acid and the science behind it.
What is Baking Soda?
Now that we’ve introduced the topic of baking soda, let’s delve deeper into its composition to understand what makes this common household item so versatile and effective.

A. baking soda composition
Baking soda, also known as sodium bicarbonate, is a white crystalline powder that is commonly used as a raising agent in baking. It is made up of sodium, hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen, and it has a slightly salty, alkaline taste. When baking soda is combined with an acid, it produces carbon dioxide gas, which causes the dough to rise. This reaction is what makes it so useful in baking.
Baking soda is a base, meaning it has a pH above 7. This property is what makes it effective in neutralizing acids, including battery acid. The chemical reaction between baking soda and an acid results in the formation of water and carbon dioxide, effectively neutralizing the acid.
B. Common uses of baking soda
Baking soda is a versatile substance with a wide range of uses. Here are some of the most common uses:
- Baking: Baking soda is used as a leavening agent in baking. It reacts with acidic components in batters, releasing carbon dioxide, which causes expansion of the batter and forms the characteristic texture and grain in pancakes, cakes, quick bread, and other baked and fried foods.
- Cleaning: Baking soda is a popular natural cleaning agent. It can be used to scrub surfaces in much the same way as commercial non-abrasive cleansers. Baking soda is also effective at removing stains and neutralizing odors.
- Health and Beauty: Baking soda has a number of health and beauty uses. It can be used as a toothpaste, deodorant, and even an antacid. It’s also a popular home remedy for acne.
- Gardening: Some gardeners use baking soda as a pesticide and as a natural fungicide. It can also be used to test the pH level of the soil.
- Neutralizing Acids: Baking soda can be used to neutralize a wide range of acids, including battery acid. This is due to its basic (alkaline) nature.
Now that we’ve understood what baking soda is and its common uses, let’s delve into the main topic of our discussion – how baking soda interacts with battery acid.
How Does Baking Soda Neutralize Battery Acid?
Baking soda, or sodium bicarbonate, is a naturally occurring substance that is capable of neutralizing acids. This property makes it a valuable tool for those who deal with battery acid.
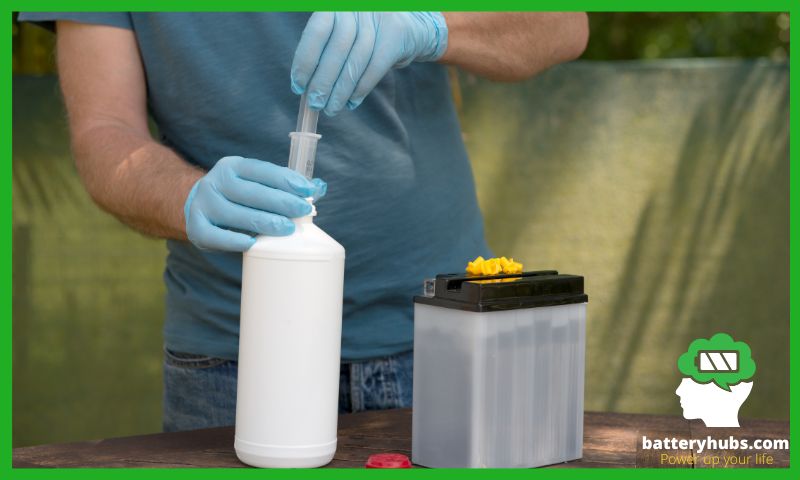

A. Chemical Reaction Between Baking Soda and Battery Acid
When baking soda comes into contact with an acid, it undergoes a chemical reaction that neutralizes the acid. The reaction between baking soda and battery acid results in the formation of water, carbon dioxide, and a salt compound. This reaction can be represented by the following chemical equation:
H2SO4 (battery acid) + 2NaHCO3 (baking soda) -> Na2SO4 (sodium sulfate) + 2H2O (water) + 2CO2 (carbon dioxide)
This reaction is exothermic, meaning it releases heat. The release of carbon dioxide gas results in the characteristic fizzing or bubbling when baking soda is added to an acid.
B. Step-by-Step Guide on How to Use Baking Soda to Neutralize Battery Acid
- Safety First: Before starting, ensure you’re wearing appropriate safety gear. This includes rubber gloves, safety glasses, and protective clothing.
- Prepare a Baking Soda Solution: Mix a few tablespoons of baking soda into a cup of water. Stir until the baking soda is completely dissolved.
- Apply the Solution: Pour the baking soda solution onto the battery acid spill. Be careful to avoid direct contact with the acid.
- Wait for the Reaction: Allow the solution to sit for a few minutes. You should see a fizzing or bubbling reaction as the baking soda neutralizes the acid.
- Clean Up: Once the reaction has stopped, use a wet/dry vacuum or absorbent material to clean up the residue. Dispose of the cleanup materials according to local regulations.
- Rinse and Dry: Rinse the area with clean water and allow it to dry completely.
Remember, while baking soda can neutralize battery acid, it’s important to handle these substances with care. Always prioritize safety and follow local regulations for handling and disposal.
Now that we’ve understood how baking soda neutralizes battery acid, let’s move on to explore some safety precautions we need to take while performing this process.
Safety Measures When Handling Battery Acid and Baking Soda
As we delve deeper into the topic of handling battery acid and baking soda, it’s crucial to underscore the importance of safety. Let’s start by discussing the essential role of personal protective equipment in ensuring your safety during this process.
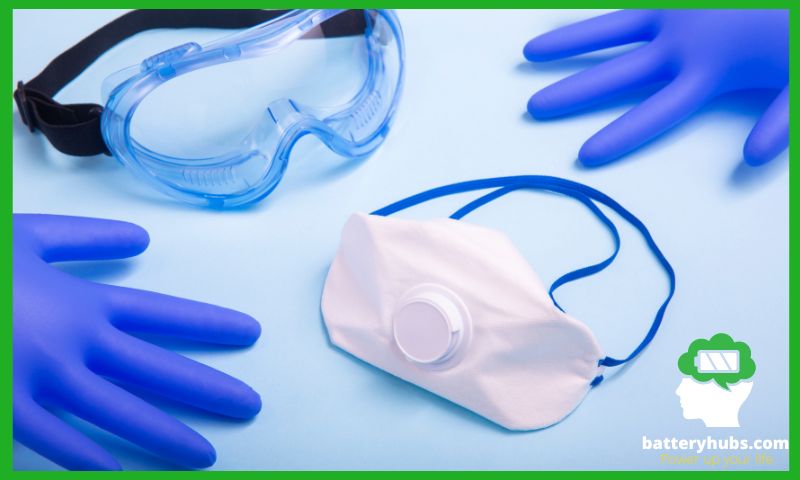
A. Importance of Personal Protective Equipment
When dealing with substances like battery acid and baking soda, it’s crucial to prioritize safety. Battery acid, being a strong acid, can cause severe burns and eye damage. On the other hand, baking soda, though generally safe, can cause irritation if it comes into contact with your eyes or if inhaled.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is a must-have when handling these substances. This includes gloves, safety goggles, and protective clothing.
Gloves protect your hands from direct contact with the substances.
Safety goggles shield your eyes from potential splashes, while protective clothing covers your skin, preventing any direct contact.
B. What to Do in Case of Skin Contact with Battery Acid or Baking Soda
Despite taking precautions, accidents can happen. If battery acid comes into contact with your skin, immediately rinse the area with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes while removing any contaminated clothing. Seek medical attention right away.
If baking soda comes into contact with your skin, wash the area with plenty of water. If irritation persists, seek medical advice. In case of eye contact, rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses if present and easy to do, then continue rinsing. If eye irritation persists, get medical advice.
Remember, safety should always be your top priority when dealing with chemicals, even those as common as battery acid and baking soda.
Does Baking Soda Prevent Battery Corrosion?
Ah, the age-old question: can humble baking soda really prevent battery corrosion? The answer, my friends, is a resounding yes! But let’s not stop there. Let’s dive into the nitty-gritty of how this works and how you can use baking soda to keep your battery corrosion-free.
How Baking Soda Can Prevent Battery Corrosion?
Battery corrosion is a common problem that can lead to decreased performance and, eventually, battery failure. It typically occurs when acid from the battery leaks out and reacts with the surrounding air, forming a white or bluish deposit around the battery terminals. This is where our trusty baking soda comes in.
Baking soda, or sodium bicarbonate, is a base. When it comes into contact with an acid (like the battery acid), it neutralizes it, preventing the acid from causing further corrosion. This is why baking soda is often recommended for cleaning battery terminals.
But don’t just take my word for it. According to Duston Maynes, an Automotive Repair Specialist at RepairSmith, “Lightly brush a mixture of warm water and baking soda on the battery terminals, but don’t pour it onto the battery”.
How to Apply Baking Soda to Prevent Battery Corrosion?
Now that we’ve established the science behind it, let’s get down to the practical part. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use baking soda to prevent battery corrosion:
- Safety first: Always wear rubber gloves and safety goggles when handling batteries. Battery acid can be harmful, so it’s important to protect yourself.
- Prepare your baking soda solution: Mix 1 cup (240 mL) of water with 1 teaspoon (4.6 g) of baking soda.
- Apply the solution: Pour half of your baking soda solution over the battery posts. If there’s a lot of corrosive buildup, let the mixture sit for at least 5 minutes before you try to scrub it off.
- Scrub away: Use a toothbrush or a battery terminal brush to scrub the posts and clean off the corrosion.
- Rinse and dry: Rinse the terminals and posts with cool water from a hose or spray bottle. Then, wipe them dry with a clean, dry rag.
- Prevent future corrosion: Apply petroleum jelly to the posts to prevent future corrosion.
And voila! You’ve just used baking soda to prevent battery corrosion. Now, isn’t that a neat trick?
But wait, there’s more! In the next section, we’ll explore how to safely dispose of battery acid and baking soda. So, stick around!
Conclusion
In our journey today, we’ve explored the fascinating world of battery acid, and baking soda, and how the two interact. We’ve learned that battery acid is a potent substance that can cause harm if not handled correctly. On the other hand, baking soda, a common household item, can neutralize this acid and even prevent battery corrosion.
We’ve also delved into the science behind this reaction and provided a step-by-step guide on how to use baking soda to prevent battery corrosion. Lastly, we’ve emphasized the importance of safety measures when handling these substances.
Remember, knowledge is power. Understanding these concepts not only helps you maintain your batteries better but also equips you with the knowledge to handle potential battery acid leaks safely. So, the next time you see some corrosion on your car battery, you know what to do. Grab that box of baking soda and get to work!
In the world of batteries, knowledge is indeed power. Understanding the intricacies of battery maintenance, such as the role of baking soda in neutralizing battery acid and preventing corrosion, can significantly enhance the lifespan of your batteries. But our exploration doesn’t stop here. There’s a whole universe of battery-related knowledge waiting to be discovered.
For instance, have you ever wondered if leaving your key fob in your car could drain your battery? Or perhaps you’re curious about how to prevent your amp from draining your battery? We’ve got you covered!
Maybe you’re interested in more advanced topics like how to recondition a sealed car battery or how a battery reconditioner works? We’ve delved into these topics as well.
And it’s not just about car batteries. We’ve also explored common issues with other types of batteries. For example, if you’re a Kindle user, you might find our article on why your Kindle is not charging when you plug it in particularly useful.
So, as we conclude our discussion on baking soda and battery acid, remember that this is just the beginning. There’s a wealth of information out there to help you understand and maintain your batteries better. Happy exploring!
FAQ
What is the chemical reaction between baking soda and battery acid?
The chemical reaction between baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) and battery acid (sulfuric acid) results in the formation of carbon dioxide gas, water, and sodium sulfate. This reaction is exothermic, meaning it releases heat. The chemical equation for this reaction is: 2NaHCO3 + H2SO4 -> Na2SO4 + 2H2O + 2CO2.
Can baking soda prevent battery corrosion?
Yes, baking soda can prevent battery corrosion. When applied to the battery terminals, baking soda neutralizes the acidic conditions that lead to corrosion. This is due to the basic nature of baking soda, which reacts with the acid to produce water and carbon dioxide, thereby reducing corrosion.
Is it safe to touch baking soda solution?
Baking soda solution is generally safe to touch. It is a mild base and does not pose a significant risk to the skin. However, prolonged contact or exposure to large amounts can cause skin irritation. Always rinse your skin thoroughly after handling the baking soda solution.
How much baking soda is needed to neutralize battery acid?
According to OSHA, battery acid can be safely neutralized with a dilution of baking soda or soda ash (one pound per gallon of water).
Where can I buy baking soda?
Baking soda can be purchased from a variety of sources. It is commonly available in grocery stores, supermarkets, and online marketplaces like Amazon. Some specific stores where you can find baking soda include Walmart, Target, and Costco. You can also find it in pharmacies like Walgreens and home improvement stores like Home Depot.
