An alkaline battery is a type of disposable battery that uses a chemical reaction between zinc, manganese dioxide, and potassium hydroxide to produce an electric current. Alkaline batteries are available in a variety of sizes, including AAA, AA, C, D, and 9V, and are commonly used in electronic devices such as remote controls, flashlights, and toys. They offer several benefits over other types of batteries, including a high energy density, long lifespan, and low cost. Proper disposal of alkaline batteries is important to avoid leaks and protect the environment.
Are you curious about the technology behind the batteries powering your electronic devices? Have you ever wondered what sets alkaline batteries apart from other types of batteries?
In this blog post, we will dive into the world of alkaline batteries, exploring their chemistry, differences from other battery types, sizes, benefits, and proper disposal methods.
We will also discuss their common uses and how to identify an alkaline battery. By the end of this post, you will have a better understanding of these versatile power sources.
Now, let’s delve into the chemistry behind alkaline batteries.
Chemistry and Construction of Alkaline Battery
Now that we have discussed the chemistry and construction of alkaline batteries, let’s take a closer look at the main components of these batteries and how they affect their performance.
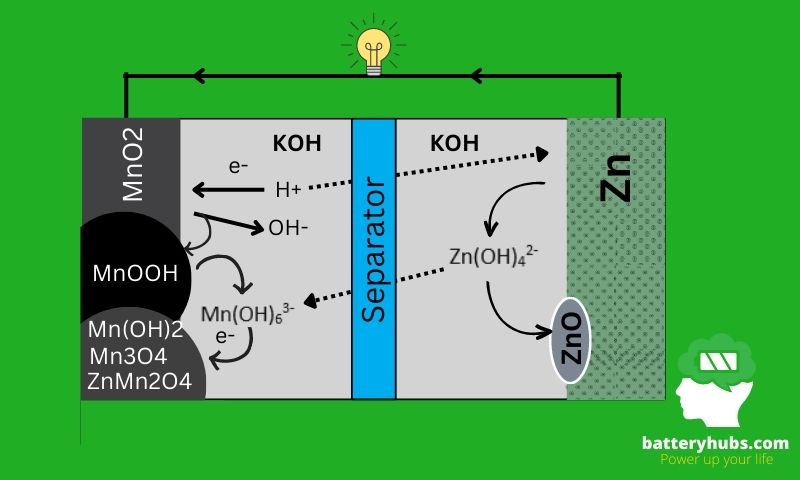
What are the main components of an alkaline battery?
Alkaline batteries consist of several key components that work together to produce an electric current. The main components of an alkaline battery include:
| Component | Function |
| Zinc | Negative electrode, or cathode |
| Manganese Dioxide | Positive electrode, or anode |
| Potassium Hydroxide | Electrolyte, allowing transfer of electrons between electrodes |
| Plastic Housing | Protects and contains the chemical components |
| Terminal Posts | Connects the battery to the device |
- Zinc: The zinc serves as the negative electrode, or cathode, in the battery.
- Manganese Dioxide: The manganese dioxide acts as the positive electrode or anode.
- Potassium Hydroxide: The potassium hydroxide serves as the electrolyte, allowing the transfer of electrons between the two electrodes.
- Plastic Housing: The plastic housing protects and contains the chemical components of the battery.
- Terminal Posts: The terminal posts connect the battery to the device, allowing the electric current to flow.
Together, these components work to create the electric current that powers electronic devices.
Chemistry in Batteries
The chemical reactions within a battery are what provide the power to run electronic devices. In an alkaline battery, chemical reactions involve the transfer of electrons from one substance to another, creating an electric current. The specific chemicals used in alkaline batteries include zinc, manganese dioxide, and potassium hydroxide, which are mixed together to create a powerful and long-lasting power source.
Alkaline Battery Chemicals
The three main chemicals used in alkaline batteries are zinc, manganese dioxide, and potassium hydroxide. These chemicals are carefully mixed together in a specific ratio to create a powerful and long-lasting power source.
| Chemical | Function |
| Zinc | Negative electrode, or cathode |
| Manganese Dioxide | Positive electrode, or anode |
| Potassium Hydroxide | Electrolyte, allowing transfer of electrons between electrodes |
The chemical reaction in an alkaline battery can be represented by the following equation:
Zn + 2MnO2 + 2KOH -> Zn(OH)2 + 2KMnO4
In this reaction, zinc (Zn) and manganese dioxide (MnO2) react with potassium hydroxide (KOH) to produce zinc hydroxide (Zn(OH)2) and potassium permanganate (KMnO4). The transfer of electrons between zinc and manganese dioxide creates the electric current that powers electronic devices.
Alkaline Battery Sizes
Alkaline batteries are available in a variety of sizes, each with its own common applications.
| Size | Common Applications |
| AAA | Remote controls, small electronic devices |
| AA | Flashlights, portable electronic devices |
| C | Toys, portable electronic devices |
| D | Power tools, larger electronic devices |
| 9V | Smoke detectors, portable electronic devices |
The most common sizes are AAA, AA, C, D, and 9V. AAA batteries are the smallest size and are commonly used in remote controls and small electronic devices. AA batteries are slightly larger and are commonly found in flashlights and portable electronic devices. C and D batteries are larger still and are used in toys and power tools, respectively. 9V batteries are the largest common size and are commonly found in smoke detectors and other portable electronic devices.
Alkaline Battery Voltage
The voltage of an alkaline battery is determined by its size. The most common sizes of alkaline batteries are AAA, AA, C, D, and 9V, and each size has a specific voltage.
| Battery Size | Voltage |
| AAA | 1.5V |
| AA | 1.5V |
| C | 1.5V |
| D | 1.5V |
| 9V | 9V |
For example, AAA, AA, C, and D batteries all have a voltage of 1.5V, while 9V batteries have a voltage of 9V. This means that AAA, AA, C, and D batteries can be used interchangeably in devices that require 1.5V, but 9V batteries cannot be used in place of the smaller sizes. It is important to choose the correct battery size and voltage for your electronic device to ensure it functions properly.
Alkaline Battery Current
The current rating of an alkaline battery indicates how much electrical current it can provide over a specific period of time.
| Battery Size | Current Rating |
| AAA | 600-700 mAh |
| AA | 1,000-1,500 mAh |
| C | 2,000-3,000 mAh |
| D | 5,000-7,000 mAh |
| 9V | 500-600 mAh |
The current rating is typically measured in milliamp-hours (mAh), and the exact rating will vary depending on the specific battery size and manufacturer.
For example, AAA batteries have a current rating of 600-700 mAh, while AA batteries have a rating of 1,000-1,500 mAh.
C batteries have a rating of 2,000-3,000 mAh, while D batteries have a rating of 5,000-7,000 mAh. 9V batteries have a lower current rating of 500-600 mAh.
When choosing an alkaline battery for your device, it is important to select a size with a current rating that meets or exceeds the device’s requirements.
Difference between Alkaline and Lead Acid Batteries
| Property | Alkaline Batteries | Lead Acid Batteries |
| Chemical Composition | Zinc, manganese dioxide, potassium hydroxide | Lead dioxide, lead, sulfuric acid |
| Energy Density | High | Low |
| Lifespan | Long | Short |
| Rechargeability | Non-rechargeable | Rechargeable |
| Cost | Inexpensive | Expensive |
As you can see from the table above, there are several key differences between alkaline and lead-acid batteries. Alkaline batteries are composed of zinc, manganese dioxide, and potassium hydroxide, while lead acid batteries are made up of lead dioxide, lead, and sulfuric acid. Alkaline batteries have a higher energy density, meaning they can provide more power per unit of weight, and have a longer lifespan than lead acid batteries.
Additionally, alkaline batteries are non-rechargeable, making them less expensive to replace than rechargeable lead-acid batteries.
What are the Benefits of Alkaline Batteries?
Alkaline batteries offer several benefits over other types of batteries. Some of the key advantages of alkaline batteries include:
- High energy density: Alkaline batteries can provide a lot of power in a small package, making them ideal for portable electronic devices.
- Long lifespan: Alkaline batteries can last for several years when not in use, making them a reliable power source.
- Inexpensive: Alkaline batteries are non-rechargeable, making them less expensive to replace than rechargeable batteries.
- Wide availability: Alkaline batteries are widely available at stores and online, making them easy to find when you need them.
- Versatility: Alkaline batteries come in a variety of sizes, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
Overall, alkaline batteries offer a convenient, reliable, and cost-effective power source for a wide range of electronic devices.
What are the Disadvantages of Alkaline Batteries?
While alkaline batteries offer several advantages over other types of batteries, there are also some disadvantages to consider. Some of the key disadvantages of alkaline batteries include:
- Non-rechargeable: Alkaline batteries are not rechargeable, so they must be replaced once they are depleted. This can be more expensive in the long run compared to rechargeable batteries.
- Limited lifespan: Alkaline batteries have a limited lifespan, even when not in use. This means they may not last as long as some other types of batteries, such as lithium-ion batteries.
- Limited temperature range: Alkaline batteries are not suitable for use in extreme temperatures, as they can lose their charge quickly in cold temperatures and become damaged in high temperatures.
- Environmental impact: While alkaline batteries can be recycled, improper disposal can lead to leaks and contamination of soil and water. This can have negative environmental impacts.
Overall, while alkaline batteries offer several benefits, they also have some limitations that should be considered when choosing a battery for a specific application.
What are Alkaline Batteries Used for?
| Application | Commonly Used Battery Sizes |
| Remote controls | AAA |
| Flashlights | AA |
| Toys | C, D |
| Power tools | D |
| Smoke detectors | 9V |
| Portable electronic devices | AAA, AA, C, D, 9V |
Alkaline batteries are used in a wide range of applications, from remote controls and flashlights to toys and power tools. The most common sizes of alkaline batteries are AAA, AA, C, D, and 9V, and each size has its own specific applications.
For example, AAA batteries are commonly used in remote controls, while AA batteries are commonly found in flashlights. C and D batteries are often used in toys and power tools, respectively. 9V batteries are commonly used in smoke detectors and other portable electronic devices.
Overall, alkaline batteries are a versatile and reliable power source for a wide range of applications.
How does an alkaline battery work?
When an alkaline battery is inserted into a device, the zinc and manganese dioxide electrodes come into contact with the electrolyte, a solution of potassium hydroxide.
The chemical reaction between zinc, manganese dioxide, and potassium hydroxide produces zinc hydroxide and potassium permanganate. This reaction can be represented by the following equation:
Zn + 2MnO2 + 2KOH -> Zn(OH)2 + 2KMnO4
As the chemical reaction takes place, electrons are transferred from the zinc to the manganese dioxide. This creates an electric current that flows through the device.
The electric current continues to flow as long as the zinc and manganese dioxide electrodes remain in contact with the electrolyte.
When the battery is depleted, the chemical reactions will no longer produce an electric current. The battery can then be disposed of properly.
In summary, an alkaline battery works by using a chemical reaction to create an electric current that powers electronic devices. The specific chemicals used in alkaline batteries, including zinc, manganese dioxide, and potassium hydroxide, work together to produce the electric current. Once the battery is depleted, the chemical reactions will no longer produce an electric current and the battery must be replaced.
How to Identify an Alkaline Battery?
There are several ways to identify an alkaline battery:
- Check the label: Most alkaline batteries will have a label that clearly indicates that they are alkaline. This label may be on the battery itself or on the packaging.
- Check the size: Alkaline batteries are available in a variety of sizes, including AAA, AA, C, D, and 9V. If the battery you are looking at is one of these sizes, it is likely an alkaline battery.
- Check the voltage: Alkaline batteries have a voltage of 1.5V for AAA, AA, C, and D sizes, and a voltage of 9V for 9V sizes. If the battery has a voltage of 1.5V or 9V, it is likely an alkaline battery.
- Check the color: Alkaline batteries are typically silver or gray in color. If the battery you are looking at is this color, it is likely an alkaline battery.
- Consult the manufacturer: If you are still unsure whether a battery is alkaline, you can contact the manufacturer to confirm. Most manufacturers will be able to provide this information.
Overall, identifying an alkaline battery is relatively simple and can be done by checking the label, size, voltage, and color of the battery. If you are unsure, you can always contact the manufacturer for confirmation.
Now that we have discussed how to identify an alkaline battery, let’s move on to the topic of leaks and disposal.
Leaks and Disposal of Alkaline Batteries
It is important to properly dispose of alkaline batteries to avoid leaks and potential damage to the environment. Here are some key points to consider when disposing of alkaline batteries:
- Do not throw alkaline batteries in the trash: Alkaline batteries contain chemicals that can be harmful to the environment if not disposed of properly. Throwing alkaline batteries in the trash can lead to leaks and contamination of soil and water.
- Recycle alkaline batteries: Many municipalities and retailers offer battery recycling programs. These programs allow you to safely and properly dispose of alkaline batteries.
- Store alkaline batteries properly: Before disposing of alkaline batteries, it is important to store them properly to avoid leaks. Alkaline batteries should be stored in a cool, dry place away from heat and moisture.
- Dispose of leaking alkaline batteries immediately: If an alkaline battery is leaking, it should be disposed of immediately to avoid potential damage to the environment. Leaking alkaline batteries should be placed in a sealed container and taken to a battery recycling center for proper disposal.
Overall, it is important to properly dispose of alkaline batteries to avoid leaks and potential harm to the environment. Recycling programs and proper storage are key to ensuring safe and responsible disposal of alkaline batteries.
Why disposal is important?
Proper disposal of alkaline batteries is important for both environmental and for financial reasons.
From an environmental standpoint, improper disposal of alkaline batteries can lead to leaks and contamination of soil and water. This can have serious consequences for wildlife and the ecosystem. By properly disposing of alkaline batteries through recycling programs, we can avoid these negative impacts and protect the environment.
From a financial standpoint, improper disposal of alkaline batteries can be costly. If alkaline batteries are not disposed of properly, they can leak and cause damage to electronic devices and other properties. This can result in costly repairs or replacements. By properly disposing of alkaline batteries, we can avoid these potential costs and save money in the long run.
Overall, proper disposal of alkaline batteries is important for both environmental and financial reasons. By recycling alkaline batteries through responsible programs, we can avoid leaks and contamination, protects the environment, and save money.
How to Disposal Alkaline battery?
To properly dispose of alkaline batteries, follow these steps:
- Identify the type of battery you are disposing of: Make sure the battery you are disposing of is an alkaline battery. Alkaline batteries are commonly used in a variety of electronic devices, including remote controls, flashlights, toys, power tools, and smoke detectors.
- Check for leaks: Before disposing of an alkaline battery, inspect it for leaks. If the battery is leaking, it should be disposed of immediately to avoid potential harm to the environment.
- Store the battery properly: Before disposing of an alkaline battery, make sure it is stored properly to avoid leaks. Alkaline batteries should be stored in a cool, dry place away from heat and moisture.
- Locate a battery recycling center: Many municipalities and retailers offer battery recycling programs. These programs allow you to safely and properly dispose of alkaline batteries. Contact your local government or a retailer to find a battery recycling center near you.
- Transport the battery to the recycling center: Once you have located a battery recycling center, transport the alkaline battery to the center for proper disposal. Make sure the battery is properly sealed and transported in a safe manner.
- Dispose of the battery: At the recycling center, the alkaline battery will be safely and properly disposed of. The chemicals in the battery will be recycled or disposed of in a responsible manner.
Overall, disposing of alkaline batteries properly is important to avoid leaks and potential harm to the environment. By following these steps, you can ensure that your alkaline batteries are disposed of safely and responsibly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, alkaline batteries are a convenient, reliable, and cost-effective power source for a wide range of electronic devices. They are composed of zinc, manganese dioxide, and potassium hydroxide, and are available in a variety of sizes to meet different power needs.
Alkaline batteries offer several benefits over other types of batteries, including a high energy density, long lifespan, and low cost. They are used in a wide range of applications, including remote controls, flashlights, toys, power tools, and smoke detectors.
Proper disposal of alkaline batteries is important to avoid leaks and protect the environment. By recycling alkaline batteries through responsible programs, we can ensure that they are disposed of safely and responsibly.
Furthermore, understanding the distinctions between alkaline batteries and other types of batteries is key to making an informed decision about your power source. For example, compared to primary batteries, alkaline batteries tend to offer a higher energy density and longer lifespan, which is beneficial for power-hungry devices. You can read more about the differences between primary batteries and alkaline batteries in our comprehensive guide on what is a primary battery.
In addition, the unique characteristics of alkaline batteries make them suitable for specific uses. A closer look at the various applications of alkaline batteries will reveal why these batteries are commonly found in devices such as remote controls, toys, and smoke detectors.
Moreover, it’s important to recognize the advantages and disadvantages of alkaline batteries. While they are generally reliable and cost-effective, there are limitations such as a limited temperature range and environmental impact that users should be aware of. Weighing these factors against the benefits of other types of batteries, such as non-alkaline batteries, can help you decide which is better for your specific needs.
Another important aspect to consider is the disposability of alkaline batteries. Unlike some other types of batteries, alkaline batteries are not rechargeable. This means that once depleted, they must be replaced. For more information about the reusability of alkaline batteries, check out our article on whether alkaline batteries can be recharged.
Finally, it’s crucial to accurately identify alkaline batteries. This is because they come in a variety of sizes and are usually marked as alkaline on the label. If you’re unsure how to identify an alkaline battery, our article provides a detailed guide to help you.
In conclusion, whether you’re deciding on which battery is alkaline for your device, curious about the pH of an alkaline battery, or wondering if all AAA batteries are alkaline, it’s essential to consider these factors to make the best choice for your power needs. By doing so, you can ensure a consistent and reliable power source for your devices, while also practicing responsible battery disposal to protect our environment.
