The term “battery” originates from Benjamin Franklin in 1748, who used it to describe a set of linked capacitors storing electrical energy. Inspired by military “batteries” of cannons, the name denotes a group of devices working together, reflecting the function of a battery to store and release energy.
As someone who’s been deeply involved in the battery industry for years, I can tell you that these little powerhouses have an absolutely fascinating history. In fact, you might not know this, but the term “battery” dates all the way back to 1749, when the legendary Benjamin Franklin himself coined it during his experiments with electricity. And trust me, there’s so much more to learn about the subject than meets the eye.
In this blog post, we’ll dive into the electric world of batteries together, uncovering the story behind the name and exploring how these essential devices have evolved over the centuries. So buckle up, my fellow battery enthusiasts, because we’re about to embark on a charged journey through time!
How Did the Term “Battery” Originate in the Context of Electricity?
As a seasoned battery expert, I’ve always been intrigued by the history of this seemingly simple word. So, let’s dive into the origins of the term “battery” in the context of electricity and uncover the story behind it!
Benjamin Franklin’s experiments with electricity
You might know Benjamin Franklin as one of the founding fathers of the United States, but did you know he was also a whiz at electrical experiments? In 1749, while tinkering with Leyden jar capacitors, Franklin was struck by a brilliant idea. He realized that by connecting several capacitors together, he could create a more powerful electrical charge. This arrangement reminded him of a military battery, and so, the term “battery” was born!
Fun Fact: Franklin’s famous kite experiment in 1752 helped prove that lightning was indeed electrical.
The use of Leyden jar capacitors
Now, you might be wondering, “What the heck is a Leyden jar capacitor?” Well, I’m glad you asked! Leyden jars were among the first devices capable of storing static electricity. Invented in the 18th century, these glass jars were lined with metal foil and could store an electric charge when a metal rod was inserted into the jar. By connecting multiple Leyden jars together, Franklin was able to create a “battery” that could produce a stronger electrical discharge.
Military origins of the term “battery”
Before it became synonymous with electricity, the term “battery” had a different meaning in the military world. It referred to a group of artillery pieces working together to bombard an enemy position. So when Franklin connected multiple Leyden jars to create a stronger charge, it seemed natural to use the same term to describe his invention. And thus, the connection between the military term “battery” and electrical devices was forged!
| Military Batteries | Electrical Batteries |
|---|---|
| Group of artillery pieces | Group of connected cells |
| Coordinate for maximum impact | Work together for stronger charge |
| Bombard enemy positions | Produce electric power |
So there you have it, the fascinating origins of the term “battery” in the context of electricity. As we’ve seen, it was a combination of Benjamin Franklin’s experiments, the use of Leyden jar capacitors, and the military concept of a battery that led to the creation of this term that we all know and love today! Now, let’s charge into the next topic with full force!
What is the Historical Significance of the Term “Battery”?
After exploring the intriguing origins of the term “battery” in the context of electricity, it’s time to dive into the historical significance of this versatile word. From its military roots to its connection with electrical devices, we’ll uncover how the term “battery” has evolved throughout history. So, let’s get cracking!
Historically, the word “battery” was used to describe a group of similar objects working together to perform a function. This concept dates back to the military usage of the term, where a battery of artillery pieces would work in unison to bombard an enemy position. This idea of a cohesive group of objects has persisted over time and has found its way into the world of electricity.
Did you know? The term “battery” has also been used to describe a group of test items, such as psychological tests or exams, that measure the same attribute or skill.
As we’ve seen, the term “battery” has strong military roots. In fact, the military usage of “battery” can be traced back to the 16th century, when artillery pieces were grouped together for strategic purposes. This concept of a battery allowed for more efficient and effective coordination, maximizing the impact of the artillery pieces on enemy positions. The military influence on the term “battery” is clear, and it has since been adapted to various contexts, including the world of electricity.
So, how did this military term make its way into the realm of electrical devices? As we learned earlier, it was Benjamin Franklin who first made the connection between the two. By linking several Leyden jars together to create a stronger electrical charge, he essentially created an electrical “battery.” This innovative concept laid the foundation for the development of modern batteries and the widespread use of the term in the context of electrical devices.
The historical significance of the term “battery” lies in its roots in military strategy and its connection to the development of electrical devices. Understanding the history behind this seemingly simple word helps us appreciate the evolution of battery technology and its impact on our modern lives. Now, as we venture forth into the electrifying world of batteries, let’s keep this rich history in mind and continue our journey of discovery!
How Has the Definition of a Battery Evolved Over Time?
As a battery enthusiast, I always find it fascinating to see how the definition and technology behind batteries have evolved over time. From their humble beginnings as simple containers for electrical energy to their essential role in powering modern devices, batteries have come a long way. So, let’s embark on a journey through time to uncover the evolution of batteries and their impact on our lives!
Early forms of batteries and their functions
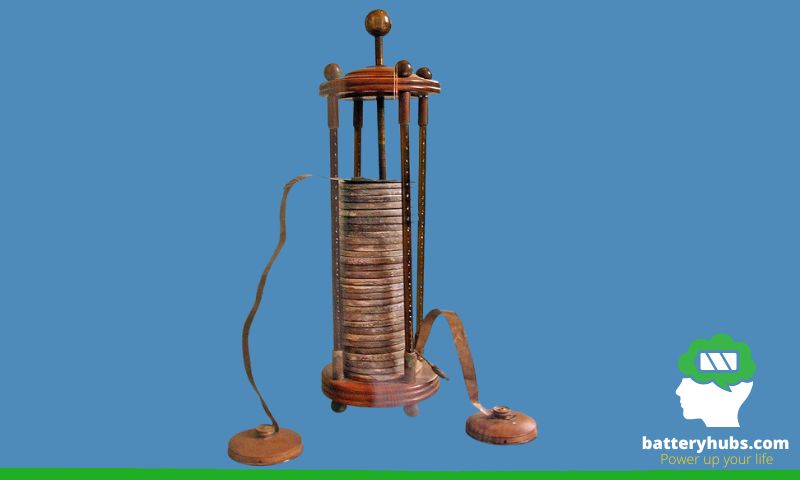

The history of batteries can be traced back to the ancient world, where early forms of electrical devices were used for various purposes. One such example is the famous Baghdad Battery, which dates back to the Parthian period (250 BCE – 224 CE). This clay jar contained a copper cylinder and an iron rod, which some believe was used to generate a weak electrical current. While the exact purpose of the Baghdad Battery remains a mystery, it highlights the presence of basic battery technology in ancient times.
The invention of the voltaic pile by Alessandro Volta
Fast forward to the late 18th century, when Italian scientist Alessandro Volta revolutionized the world of batteries with the invention of the voltaic pile in 1800. This groundbreaking device consisted of alternating layers of zinc and copper discs separated by pieces of cardboard soaked in saltwater. The voltaic pile was the first true battery, capable of producing a steady, continuous electrical current. Volta’s invention laid the groundwork for the development of modern batteries and their countless applications.
Modern battery technology and its applications
Since Volta’s time, battery technology has advanced by leaps and bounds. Today, we have a wide variety of battery types, such as alkaline, lithium-ion, and lead-acid batteries, each with their own unique characteristics and applications. Modern batteries power everything from smartphones and electric vehicles to renewable energy storage systems and space missions. The impact of battery technology on our daily lives is immense, and it continues to drive innovation and shape the future of energy storage.
| Battery Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Alkaline | Affordable, widely available | Not rechargeable, limited energy density |
| Lithium-ion | High energy density, rechargeable | Expensive, safety concerns |
| Lead-acid | Inexpensive, reliable | Heavy, low energy density |
In conclusion, the definition of a battery has evolved significantly over time, from early electrical devices like the Baghdad Battery to the diverse range of modern battery technologies that power our world today. As we continue to push the boundaries of energy storage, I can’t help but feel excited about what the future holds for batteries and their impact on our lives. Now, let’s charge forward and see where our curiosity takes us next!
What are the Different Types of Batteries and How Do They Work?
As a long-time battery enthusiast, I’ve had the pleasure of exploring the ins and outs of various battery types and their workings. With a diverse range of battery chemistries available today, it can be quite a challenge to understand the differences between them and how they function. So, let’s dive into the electrifying world of batteries and uncover the science behind these essential energy storage devices!
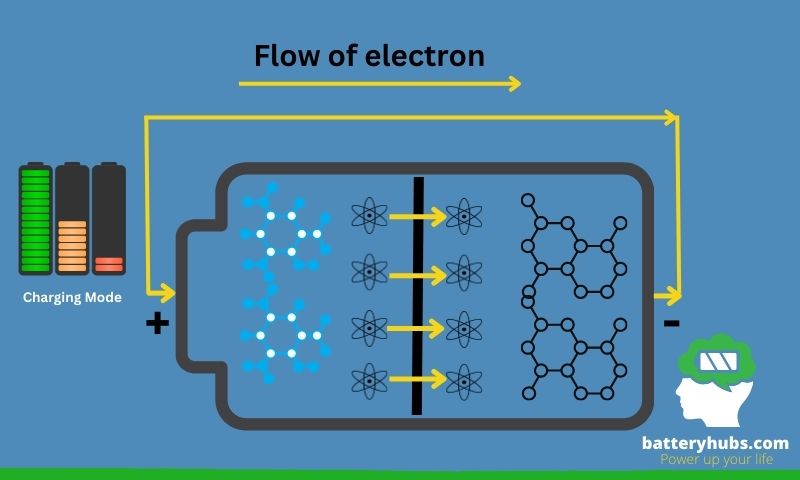
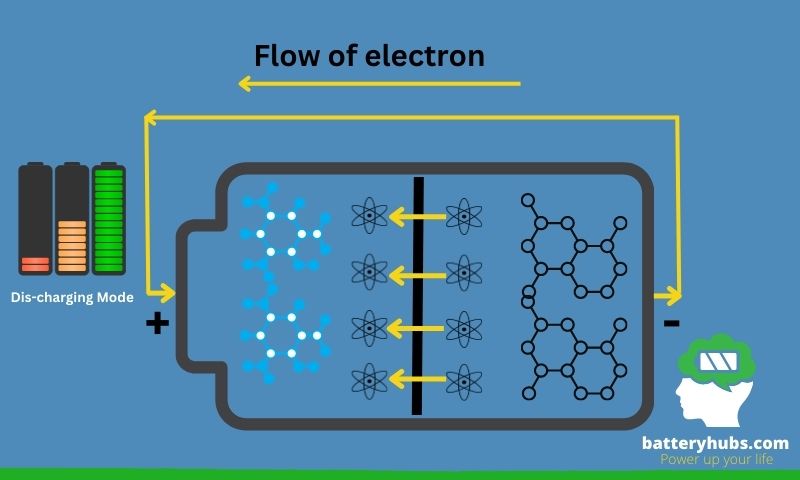
Primary and secondary batteries
Batteries can be broadly classified into two categories: primary and secondary batteries. Primary batteries, also known as single-use or disposable batteries, generate an electric current through an irreversible electrochemical reaction. Once depleted, these batteries cannot be recharged and must be discarded. Some common examples include alkaline and zinc-carbon batteries.
Secondary batteries, on the other hand, are rechargeable and can be used multiple times. They store energy through reversible electrochemical reactions, allowing them to be recharged when depleted. Some popular examples are lithium-ion, lead-acid, and nickel-metal hydride batteries.
Common battery chemistries, such as alkaline, lithium-ion, and lead-acid
Let’s take a closer look at some of the most common battery chemistries and their unique characteristics:
- Alkaline batteries are primary batteries with a long shelf life and excellent performance at room temperature. They are commonly used in household devices like remote controls and toys. However, they have limited energy density and are not rechargeable.
- Lithium-ion batteries are secondary batteries known for their high energy density, lightweight design, and long cycle life. They are widely used in smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles. While lithium-ion batteries offer numerous advantages, they can be expensive and require careful handling due to safety concerns.
- Lead-acid batteries are another type of secondary battery, often used in automotive and backup power applications. They are relatively inexpensive and reliable but have lower energy density and are heavier compared to other battery chemistries.
The role of batteries in renewable energy storage and electric vehicles
Batteries play a crucial role in the transition to renewable energy sources and the growth of electric vehicles. Energy storage systems powered by batteries enable us to store excess electricity generated from solar panels and wind turbines for later use, providing a reliable supply of clean energy even during periods of low generation.
Moreover, the advancements in battery technology have fueled the rise of electric vehicles, reducing our dependence on fossil fuels and minimizing greenhouse gas emissions. The ongoing development of more efficient and cost-effective battery technologies promises to further revolutionize the way we power our homes, businesses, and transportation systems.
Understanding the different types of batteries and their workings is essential for making informed decisions about the best energy storage solutions for our needs. From primary and secondary batteries to alkaline, lithium-ion, and lead-acid chemistries, each battery type offers unique advantages and disadvantages. With batteries playing a critical role in renewable energy storage and electric vehicles, the future of energy storage looks brighter than ever, and I can’t wait to see what exciting innovations lie ahead!
How Can Understanding the History of Batteries Help Us Innovate for the Future?
As someone who’s been fascinated by batteries for years, I can’t stress enough how important it is to understand the history of batteries and learn from past inventions and discoveries. By examining the evolution of battery technology, we can gain insights into the challenges and successes that have shaped this field, helping us to drive further innovation and create revolutionary energy storage solutions. So, let’s take a trip down memory lane and explore how the history of batteries can inspire us to build a brighter future!
The importance of learning from past inventions and discoveries
The story of batteries is filled with groundbreaking discoveries and ingenious inventions, which have laid the foundation for modern battery technology. By studying the history of batteries, we can appreciate the creativity and determination of early pioneers like Alessandro Volta, who invented the first true battery, the Voltaic Pile, in 1800.
As we look back at these milestones, we can learn valuable lessons from the challenges that inventors faced and the solutions they developed. By embracing this knowledge, we can avoid making the same mistakes and build on their achievements to create more efficient, sustainable, and affordable battery technologies.
Technological advancements in battery technology
Throughout history, innovations in battery technology have revolutionized various aspects of our lives, from communication and transportation to renewable energy and consumer electronics. For instance, the invention of the rechargeable lead-acid battery in 1859 by Gaston Planté paved the way for the development of automotive and backup power systems. Similarly, the introduction of lithium-ion batteries in the early 1990s transformed portable electronics and electric vehicles.
By understanding the impact of these technological advancements, we can identify areas where new battery technologies have the potential to make a significant difference and focus our efforts on addressing these challenges.
The potential for new battery technologies to revolutionize energy storage and consumption
The future of batteries holds great promise, with cutting-edge research and development underway to create innovative energy storage solutions. From solid-state batteries and flow batteries to advanced lithium-ion chemistries and beyond, these emerging technologies have the potential to revolutionize the way we store and consume energy.
By drawing inspiration from the history of batteries and understanding the technological advancements that have shaped this field, we can continue to push the boundaries of innovation, developing cleaner, more efficient, and more sustainable energy storage solutions for generations to come.
The history of batteries provides us with invaluable insights into the innovations and discoveries that have shaped this field. By studying the past and learning from the achievements and challenges of early pioneers, we can drive further innovation and develop groundbreaking battery technologies that will revolutionize energy storage and consumption for a more sustainable future. As a battery enthusiast, I’m thrilled to be part of this journey and can’t wait to see what the future holds for this exciting field!
Conclusion
In this fascinating exploration of the world of batteries, we’ve delved into the origins of the term “battery,” its historical significance, how the definition has evolved, and the various types of batteries available today. We’ve also discussed the importance of understanding the history of batteries to help us innovate for the future. By appreciating the creativity and determination of early inventors and learning from their achievements, we can continue to push the boundaries of battery technology, developing cleaner, more efficient, and more sustainable energy storage solutions for generations to come.
As we continue to explore the exciting world of batteries, I encourage you to check out some of our other informative articles on how batteries work, how electricity travels from a battery, the form of energy that batteries store, how a battery works in a circuit, and how rechargeable batteries function. You can also find information on recharging rechargeable batteries, how long rechargeable batteries last when in use, and even how AA batteries work. By expanding our knowledge and understanding of batteries, we can continue to drive innovation and develop more efficient and sustainable energy storage solutions for a brighter future.
FAQ
Why is it called battery in law?
Battery in the legal sense comes from the verb “to batter,” meaning “to strike or pound with hard blows.” The word “batter” in this sense derives from the Old French “baterie,” which means “the action of beating.”
How was the battery named?
The battery was named by Benjamin Franklin in 1749 when he was experimenting with electricity. He used the term “battery” to describe a group of Leyden jars used in his experiments.
Why is it called battery not cell?
It is called a battery because it consists of more than one cell. In some appliances where more power is required, a battery, or a collection of cells, is used instead of a single cell.
What is the origin of the term battery?
The term battery has its origin in the Old French word “baterie,” which means “the action of beating.” This later shifted in meaning to describe a group of similar objects functioning together, such as a battery of artillery or a group of Leyden jars used in Benjamin Franklin’s experiments.
